Cit bank 1099 int – CIT Bank 1099-INT forms are crucial for understanding your interest income and accurately filing your taxes. This guide dissects everything you need to know about these forms, from deciphering the information they contain to navigating the potential tax implications and resolving any discrepancies. We’ll cover various CIT Bank account types, interest reporting methods, and provide practical examples to clarify the process.
Mastering this information empowers you to confidently manage your finances and ensure tax compliance.
Understanding your CIT Bank 1099-INT is crucial for accurate tax reporting. Remember that large interest payments might necessitate multiple transactions, so it’s wise to be aware of the CIT Bank ACH transfer limits to avoid delays. Knowing these limits helps ensure your 1099-INT reflects all your interest income correctly and smoothly.
We’ll explore the different scenarios where you might receive a 1099-INT, such as interest earned on high-yield savings accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other interest-bearing accounts. We’ll also delve into the tax implications of this interest income, including how it affects your tax liability, potential deductions, and how to accurately report it on your tax return. This comprehensive guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the complexities of CIT Bank 1099-INT forms with ease.
Understanding CIT Bank 1099-INT Forms
Navigating the world of 1099-INT forms from CIT Bank can feel a bit like deciphering ancient scrolls, but don’t worry, we’re here to break it down in a way that’s both clear and, dare we say,
-stylish*. This guide will help you understand what a 1099-INT is, what information it contains, and how to handle it like a tax pro.
Purpose of a CIT Bank 1099-INT Form
The CIT Bank 1099-INT form is a crucial document that reports the total amount of interest income you earned from your CIT Bank accounts during the tax year. It’s your official record for the IRS, ensuring accurate reporting of your interest income.
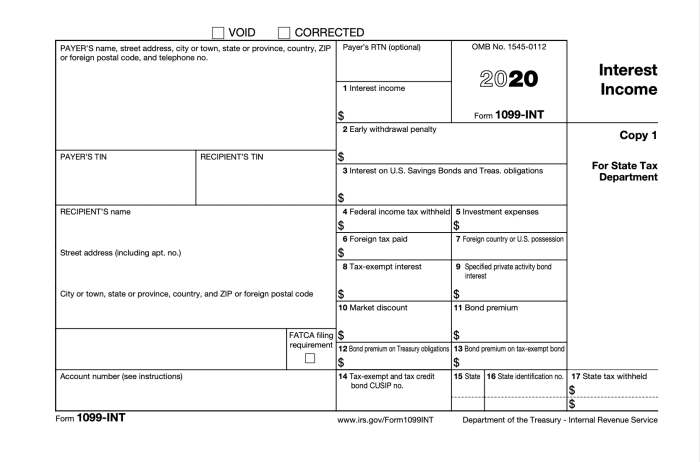
Information Included on a CIT Bank 1099-INT
Source: investopedia.com
A typical CIT Bank 1099-INT includes key details such as your name, address, taxpayer identification number (TIN), the amount of interest earned, and the payer’s (CIT Bank’s) identification information. Accuracy is key here, so double-check everything.
Scenarios Requiring a CIT Bank 1099-INT

Source: awesomefintech.com
You’ll receive a 1099-INT from CIT Bank if you earned at least $10 in interest income from any of your accounts with them. This could include interest from savings accounts, checking accounts with interest features, money market accounts, or certificates of deposit (CDs).
Organizing and Storing 1099-INT Forms
Keep your 1099-INT forms organized and in a safe place. A dedicated tax folder or a secure digital storage system is recommended. Consider scanning your forms for backup purposes and make sure you keep them for at least three years after filing your taxes.
Key Data Points on a 1099-INT Form

Source: investopedia.com
| Data Point | Description | Example | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Payer’s Name | The name of the bank issuing the form (CIT Bank) | CIT Bank | Identifies the source of your interest income |
| Your Name and Address | Your personal information as registered with the bank | [Your Name], [Your Address] | Ensures correct recipient identification |
| Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) | Your Social Security Number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN) | XXX-XX-XXXX | Crucial for tax reporting purposes |
| Interest Income | Total interest earned during the tax year | $1,200.00 | The amount you’ll report on your tax return |
Tax Implications of CIT Bank Interest Income
Understanding the tax implications of your CIT Bank interest income is crucial for accurate tax filing. Let’s explore how this income affects your overall tax liability and what deductions might be available to you.
Impact of Interest Income on Tax Liability
Interest income reported on your 1099-INT is considered taxable income. This means it’s added to your other income sources to determine your total taxable income and your tax bracket. The higher your income, the higher your tax rate.
Tax Brackets and Interest Income Taxation
The US federal income tax system uses a progressive system of tax brackets. Your interest income is taxed at the rate corresponding to your overall tax bracket, which is determined by your total income, including interest income, wages, and other sources.
Tax Treatment Compared to Other Income Types, Cit bank 1099 int
Interest income from CIT Bank is treated similarly to other forms of investment income, such as dividends. However, the specific tax rates and any applicable deductions might vary depending on the type of investment.
Potential Tax Deductions Related to Interest Income
While interest income is generally taxable, there are limited circumstances where you might be able to deduct certain interest expenses. Consult a tax professional for personalized advice on this matter.
Reporting Interest Income on a Tax Return
Reporting interest income from CIT Bank is typically done using Form 1040, Schedule B (Interest and Ordinary Dividends). You’ll need your 1099-INT to accurately complete this form.
- Gather your 1099-INT form from CIT Bank.
- Obtain Form 1040 and Schedule B.
- Accurately transfer the interest income amount from your 1099-INT to Schedule B.
- Complete the rest of Form 1040, including other income sources.
- File your tax return by the April 15th deadline (or the extended deadline if applicable).
CIT Bank Account Types and Interest Reporting
CIT Bank offers a variety of accounts that can generate interest income. Understanding how interest is reported for each account type is essential for accurate tax preparation.
Account Types, Interest Rates, and Reporting
- High-Yield Savings Account: Interest rates vary, typically reported annually on a 1099-INT.
- Money Market Account: Interest rates fluctuate, reported annually on a 1099-INT.
- Certificate of Deposit (CD): Fixed interest rate for a specific term, reported annually on a 1099-INT.
- Checking Account (with interest): Interest rates are generally lower, reported annually on a 1099-INT if the interest earned exceeds $10.
Calculating Total Interest Earned from Multiple Accounts
To calculate your total interest earned, simply add the interest amounts reported on each of your 1099-INT forms from CIT Bank. This total will be the amount you report on your tax return.
Potential Issues and Solutions Related to CIT Bank 1099-INT Forms
While receiving a 1099-INT is usually straightforward, potential issues can arise. Knowing how to handle these situations will save you stress and ensure accurate tax filing.
Potential Problems with 1099-INT Forms
Problems can include receiving an incorrect amount, a missing form, or discrepancies between your records and the 1099-INT. Addressing these promptly is crucial.
Resolving Discrepancies or Errors
If you notice an error, contact CIT Bank’s customer support immediately to initiate a correction. Keep detailed records of your communication and any supporting documentation.
Contacting CIT Bank Customer Support
CIT Bank provides various contact methods, including phone, email, and online chat. Be prepared to provide your account information and details about the discrepancy.
Common Tax Filing Mistakes and Corrections
Common mistakes include misreporting the interest amount or failing to include the interest income altogether. Correcting these errors involves filing an amended tax return (Form 1040-X).
Steps to Take if a 1099-INT is Missing or Incorrect
A flowchart illustrating the steps to take is beyond the scope of this text-based response. However, contacting CIT Bank customer support immediately is the first and most important step.
Illustrative Examples of CIT Bank 1099-INT Scenarios: Cit Bank 1099 Int
Let’s illustrate how 1099-INT forms work with some real-world examples.
Scenario: High-Yield Savings Account
- Account Details: High-yield savings account with an annual interest rate of 4%, earning $1500 in interest.
- Tax Implications: The $1500 will be reported on a 1099-INT and included as taxable income on your tax return.
Scenario: Certificate of Deposit (CD)
- Account Details: A 1-year CD with a 3% interest rate, earning $750 in interest.
- Tax Implications: The $750 will be reported on a separate 1099-INT form and included in your taxable income.
Scenario: Multiple 1099-INT Forms
- Account Details: Multiple accounts—a savings account earning $500 and a CD earning $1000.
- Tax Implications: Two 1099-INT forms will be issued, one for each account. The total interest income of $1500 will be reported on your tax return.
Last Recap
Understanding your CIT Bank 1099-INT form is vital for accurate tax reporting and financial management. By grasping the information provided, the tax implications involved, and the various account types that generate interest income, you can confidently navigate the process and avoid potential pitfalls. Remember to organize your forms, keep accurate records, and don’t hesitate to contact CIT Bank customer support if you encounter any issues.
Proactive financial management ensures a smoother tax season and provides a clearer picture of your overall financial health.